Google has rolled out an update to the Chrome browser that includes more secure password protection in the case of a data breach, real time phishing protection, predictive phishing protection and small UI tweaks to make it easier to see what used account is being used.
Password protection was developed as a separate extension by Google for Chrome earlier this year which was integrated into the Google account in October. Now Google is updating the feature to ensure your accounts stay protected during data breaches.
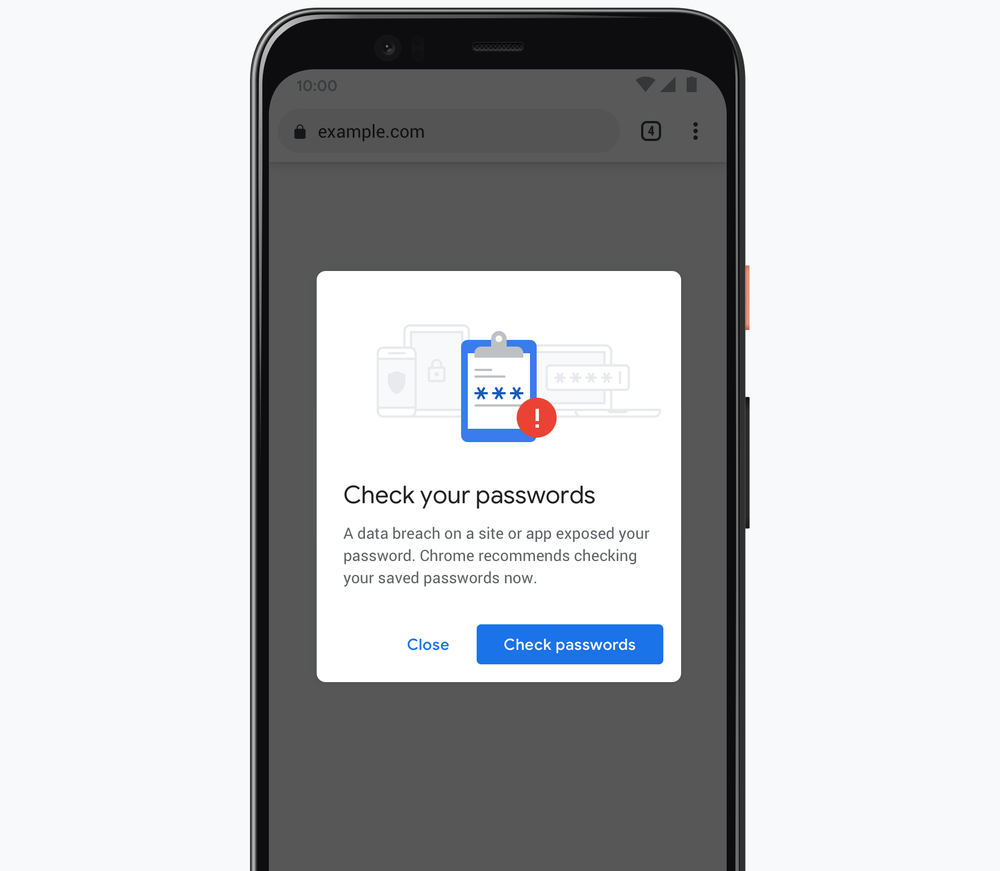
When Google discovers a users account was compromised in a data breach, Chrome will automatically notify you and strongly suggest you to change the passwords. The way Google identifies if your account is compromised involves an encrypted technique called private set intersection with blinding which ensures user privacy is maintained throughout the entire process.
The second update involves making phishing techniques work in real time. Google refreshes its list of phishing websites every 30 minutes which works with the Safe Browsing feature in Chrome to ensure users aren’t exposed to these malicious websites.
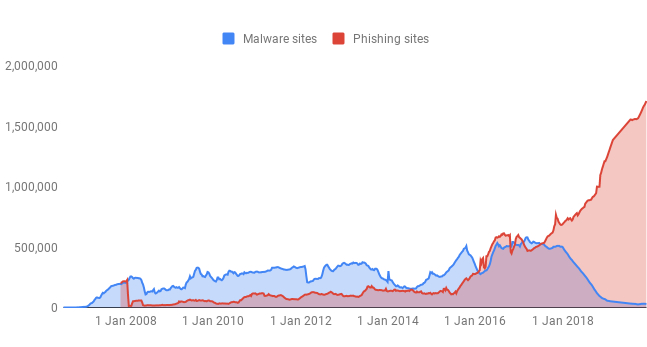
In case a website manages to get through within that 30 minute window, Chrome now offers real-time phishing protections on desktop, which warn you when visiting malicious sites in 30 percent more cases. Users will be required enable the “Make searches and browsing better” setting in Chrome.
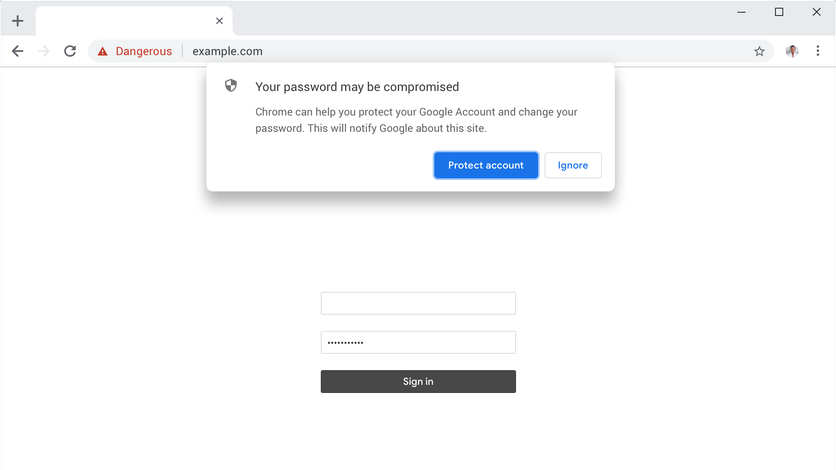
Google has also made the integration of password protection and predictive phishing as a default feature in Chrome. Earlier the option was only enabled if Sync was enabled. Now all users will get a prompt for all passwords you store in Chrome’s password manager if used on a suspected phishing site.

The last update to Chrome is a small UI tweak in the browser. Google will run a small animation showing a visual representation of the profile you’re currently using, so you can be sure you are saving your passwords to the right profile.
Google will roll out all these features to everyone gradually over the coming weeks. You can learn about these security features in more detail at Google’s Security blog here.
