
Google has opened early access to its new conversational AI service, Bard, which runs on LaMDA and aims to compete with ChatGPT. The company describes the project as an early experiment that allows users to collaborate with generative AI.
This latest development is part of Google’s ongoing effort to bring helpful AI experiences to individuals, businesses, and communities.
Open access to Bard
Google’s new AI language model, Bard, is being rolled out slowly with no set date for full public access. Similar to OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Microsoft’s Bing chatbot, Bard provides users with a blank text box to ask any questions they desire.
However, given the potential for these bots to generate false information, Google emphasizes that Bard is not a replacement for its search engine, but an extra tool to complement it. Users can use Bard to brainstorm ideas, create writing drafts, or simply have a chat about anything.
Bard is powered by a research large language model (LLM)
Bard is an innovative tool powered by a Language Model developed by Google called LaMDA. It predicts responses to prompts by selecting the most probable words one at a time. However, creativity is still factored in to avoid mundane responses.
Bard is grounded in Google’s quality information standards and will be updated with newer and better models over time. The more people use Bard, the better it becomes at predicting helpful responses.
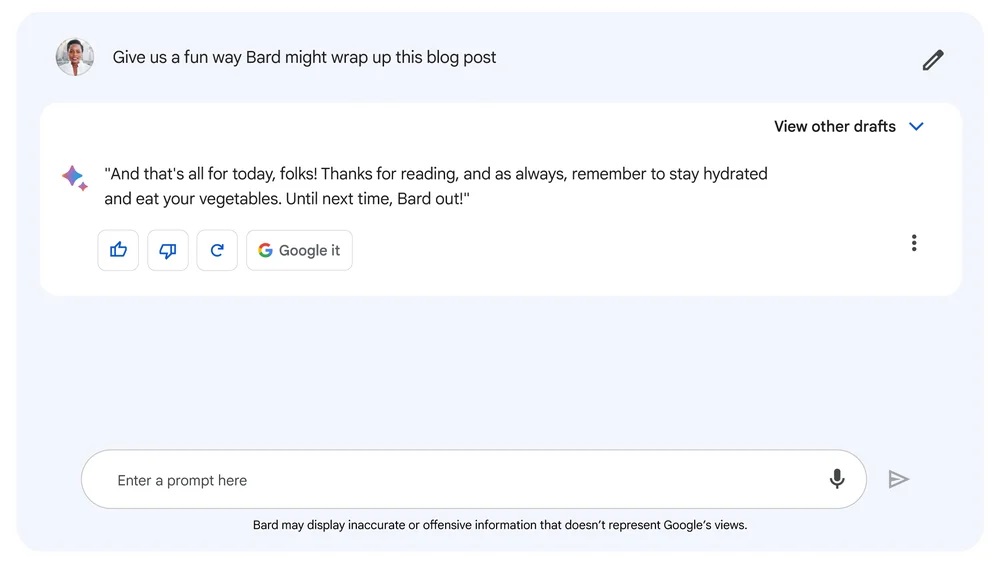
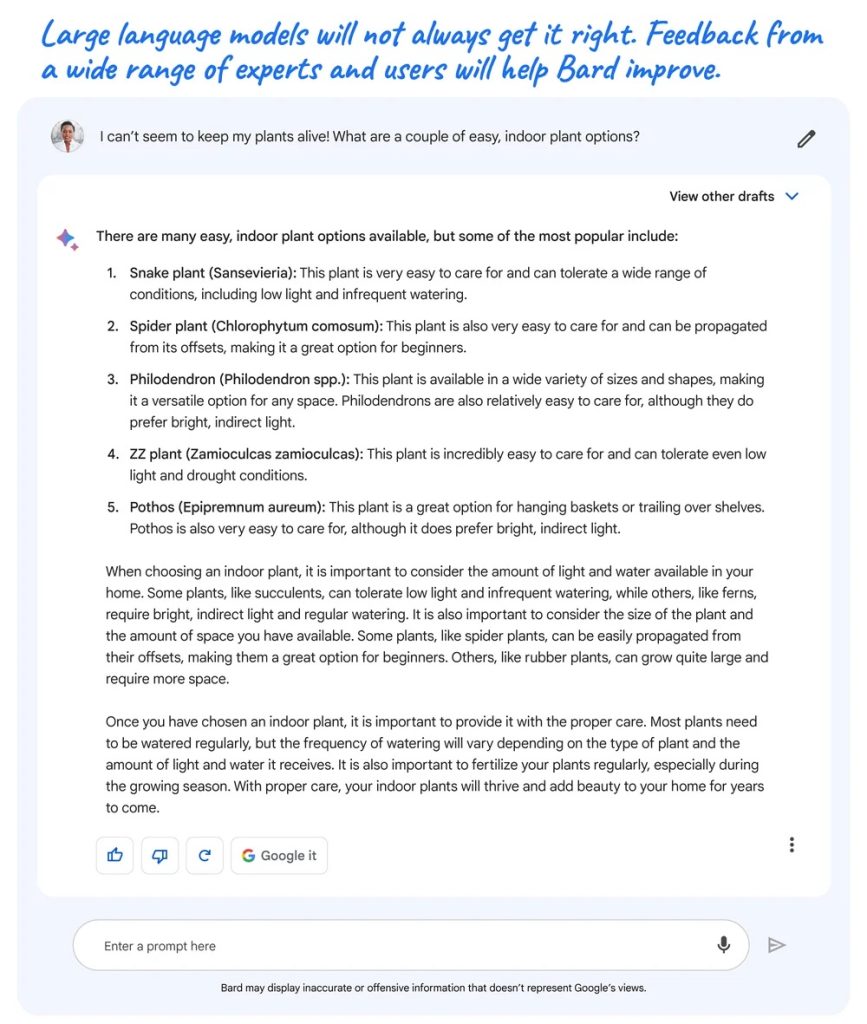
Google warns that while LLMs are exciting, they have faults. These models learn from data that may contain real-world biases and stereotypes, leading to inaccurate or misleading outputs. Bard, a language model, confidently suggested easy indoor plants but got some information wrong.
Integration of LLMs into Search
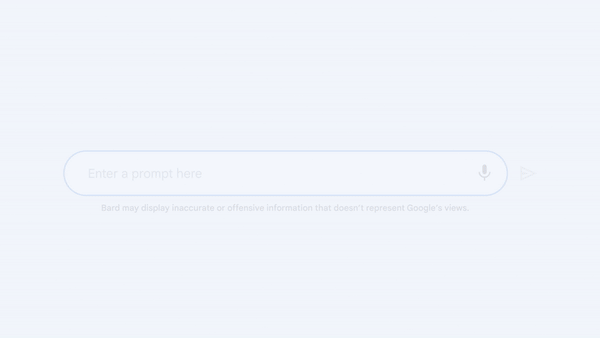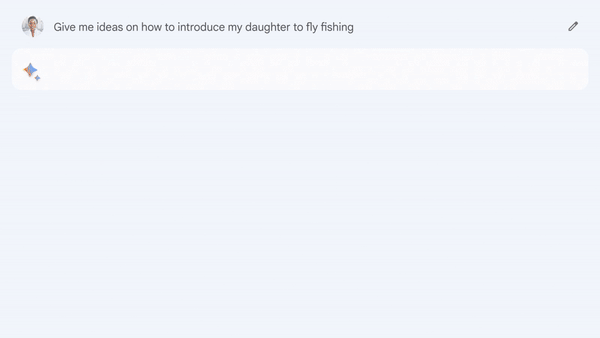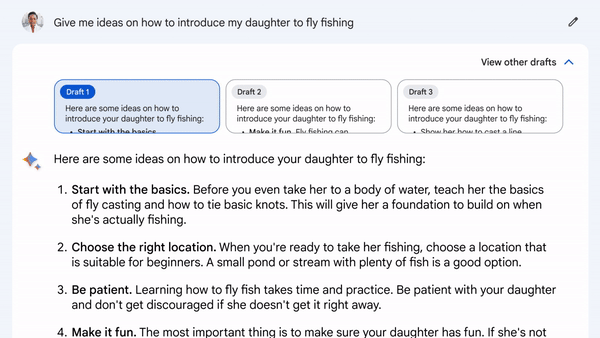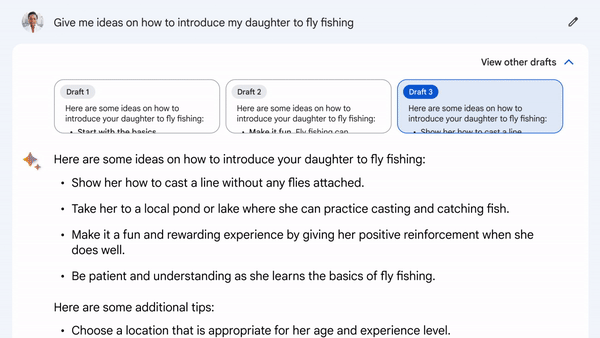
Google emphasizes the benefits of using LLMs, despite the challenges they pose. These benefits include increased productivity, creativity, and curiosity. With Bard, users have access to multiple response drafts, allowing them to select the best starting point. Collaboration with Bard can continue through follow-up questions, and users can always request another attempt if needed.
Bard is a complementary tool to Google Search, serving as a direct interface to an LLM. With Bard, users can seamlessly navigate between searching on Google and checking its responses, or exploring sources across the web. By clicking “Google it,” users can access query suggestions and relevant results in a new tab. Google has also announced plans to integrate LLMs into Search more deeply in the future.
Google is committed to building Bard responsibly, guided by its AI Principles
The tech giant prioritizes quality and safety in its development process, utilizing human feedback and evaluation to improve its systems. To maintain helpful and on-topic interactions, Google has put guardrails in place, such as capping the number of exchanges in a dialogue. With a focus on responsible development, Google is paving the way for ethical AI.
Sign up now to try Bard
Try Bard now by signing up at bard.google.com. Google is launching access in the U.S. and U.K. today, with plans to expand to more countries and languages soon.
Announcing the early access of Bard, Sissie Hsiao VP, Product and Eli Collins, VP, Research, Google, said,
You can use Bard to boost your productivity, accelerate your ideas and fuel your curiosity. You might ask Bard to give you tips to reach your goal of reading more books this year, explain quantum physics in simple terms or spark your creativity by outlining a blog post. We’ve learned a lot so far by testing Bard, and the next critical step in improving it is to get feedback from more people.
We’ll continue to improve Bard and add capabilities, including coding, more languages and multimodal experiences. And one thing is certain: We’ll learn alongside you as we go. With your feedback, Bard will keep getting better and better.
