
Apple has announced a major upgrade to the security of iMessage with the introduction of PQ3, a new cryptographic protocol aimed at enhancing end-to-end secure messaging.
iMessage with PQ3
PQ3, designed by Apple to defend against quantum attacks, offers Level 3 security, surpassing other widely used messaging apps. Since its launch in 2011, iMessage has continuously enhanced its encryption, recently transitioning to Elliptic Curve cryptography (ECC) and strengthening encryption key protection on devices.
Apple also noted that while some messaging apps, like Signal, have started incorporating post-quantum security, these efforts typically focus only on the initial key establishment, leaving ongoing message exchange vulnerable to advanced attacks.
To address these limitations, Apple aims for Level 3 security in iMessage, ensuring both initial key establishment and ongoing message exchange are protected with post-quantum cryptography.

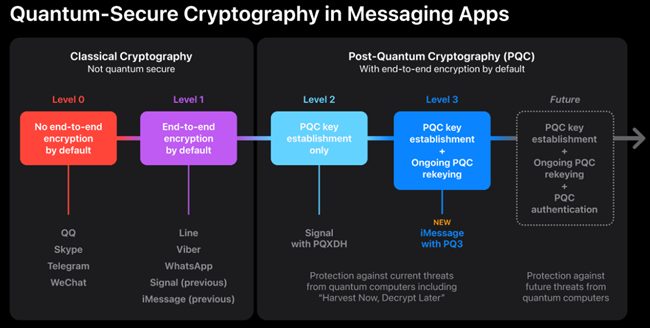
Apple cited that with PQ3, iMessage sets a new standard in messaging security, offering robust defense against quantum attacks.
Designing PQ3
PQ3 was not just a simple algorithm swap; Apple redesigned the iMessage cryptographic protocol to meet specific criteria:
- Introduction of post-quantum cryptography from the start of conversations.
- Limiting the impact of key compromises.
- By combining new post-quantum algorithms with existing Elliptic Curve algorithms, Apple employs a hybrid design for enhanced security.
- Ensuring minimal additional overhead from added security.
- Employing formal verification methods to ensure protocol security.
PQ3 employs a hybrid design, combining Elliptic Curve cryptography with post-quantum encryption, both during initial key establishment and rekeying. This additive approach ensures enhanced security and benefits from the experience gained from deploying ECC.
Constructing the PQ3 Protocol
Post-Quantum Key Establishment: iMessage allows multiple device registration, each generating its encryption keys. Public keys are registered with Apple’s Identity Directory Service (IDS).
During session establishment, devices query IDS for the recipient’s key bundle, validating it using Contact Key Verification. Public encryption keys are then used to share symmetric keys between devices.
Post-Quantum Rekeying: PQ3 implements periodic post-quantum rekeying within conversations, ensuring future messages’ security. This mechanism self-heals from key compromise, providing robust protection against adversaries.
Padding and Encryption: PQ3 adds padding to messages before encryption to prevent information leakage about message size. Messages are encrypted with AES-CTR using keys derived from message keys.
Authentication: Each message is signed with ECDSA using device authentication keys. The receiving device verifies the sender’s identifier and other fields, ensuring message integrity.
With all these, PQ3 represents a significant stride in securing end-to-end encrypted messaging, aligning with Apple’s commitment to privacy.
Availability
It’s set to roll out with iOS 17.4, iPadOS 17.4, macOS 14.4, and watchOS 10.4 releases, progressively replacing existing protocols within supported conversations.
