
ISRO successfully launched its latest Earth Observation Satellite, EOS-08, aboard the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)-D3. The launch took place today at 9:17 AM from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.
The mission’s primary focus is the design and development of a microsatellite, along with payload instruments compatible with the microsatellite bus and new technologies needed for future operational satellites.
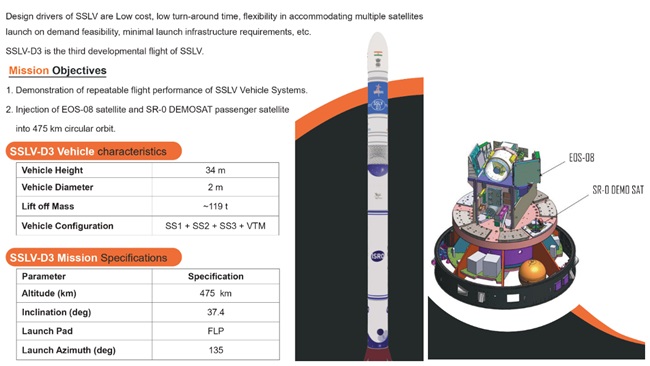
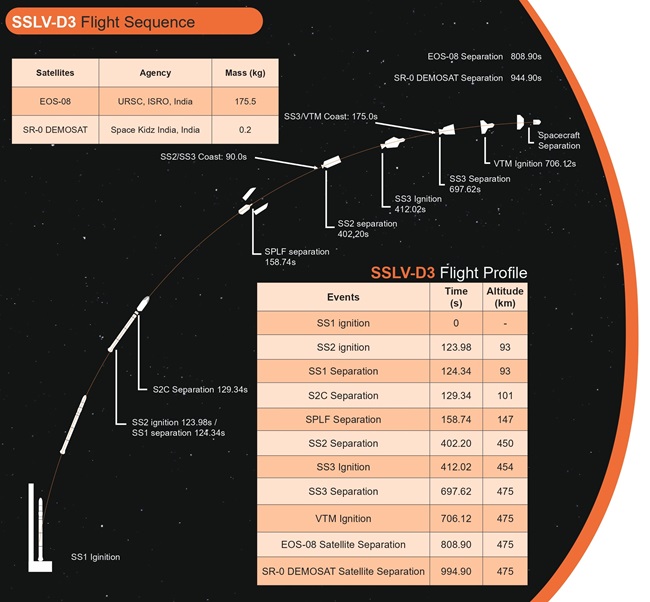
Mission Details: SSLV-D3/EOS-08
The EOS-08 satellite, built on ISRO’s Microsat/IMS-1 bus, carries three key payloads: an Electro Optical Infrared Payload (EOIR), a Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry payload (GNSS-R), and a SiC UV Dosimeter.
These payloads are integral to various applications, including satellite-based surveillance, disaster monitoring, environmental observation, and more.

EOIR Payload: This instrument captures images in the Mid-Wave IR (MIR) and Long-Wave IR (LWIR) bands, day and night. It supports applications such as disaster monitoring, environmental surveillance, fire detection, and industrial disaster observation.
GNSS-R Payload: Demonstrating remote sensing capabilities, this payload focuses on ocean surface wind analysis, soil moisture assessment, cryosphere studies, flood detection, and inland waterbody monitoring.
SiC UV Dosimeter: This sensor tracks UV irradiance at the Crew Module’s viewport in the Gaganyaan Mission and acts as a high-dose alarm for gamma radiation.
The satellite functions in a Circular Low Earth Orbit (LEO) at an altitude of 475 km, with an inclination of 37.4°. It has a mission lifespan of one year, a mass of roughly 175.5 kg, and produces about 420 W of power.
Advanced Technologies in EOS-08
EOS-08 introduces several innovative technologies in satellite mainframe systems.
The Integrated Avionics system, known as the Communication, Baseband, Storage, and Positioning (CBSP) Package, is a key highlight, combining multiple functions into a single unit and supporting up to 400 Gb of data storage.

Other advancements include:
Miniaturized Design: The satellite features a Micro-Dual Gimbal Antenna (mDGA) with a rotational speed of 6°/s and a pointing accuracy of ±1°. The phased array antenna and flexible solar panel, with a foldable substrate and lightweight materials, enhance communication capabilities and structural integrity.
Thermal Management: A pyrolytic graphite sheet diffuser plate with a high thermal conductivity of 350 W/mK is used for effective thermal management, reducing overall mass.
Integration Techniques: The mission adopts a hinge-based fixture for integrating housekeeping panels, significantly reducing the Assembly, Integration, and Testing (AIT) phase duration.
Novel Mainframe Schemes
The EOS-08 mission incorporates several new schemes in satellite technology:
- X-Band Data Transmission: Utilizes pulse shaping and Frequency Compensated Modulation (FCM) for enhanced data transmission.
- Battery Management: SSTCR-based battery charging and bus regulation operate at a frequency of 6 Hz, optimizing power usage.
- Indigenization and Innovation: The mission includes indigenized solar cell fabrication, Nano-Star Sensor use for microsat applications, vibration isolation for reaction wheels, and advanced thermal materials like Germanium Black Kapton and STAMET (Si-Al Alloy) Black Kapton.
Mission Enhancements
The capabilities of ISRO’s IMS-1 Bus system have been significantly improved in the EOS-08 mission.
- These include enhanced power generation (16% increase), more payload mass (33% increase), a fivefold increase in data download rate, and twelve times more data storage.
- Additionally, the mission management system features an auto-launch pad initialization capability.
EOS-08 represents a significant step forward in ISRO’s satellite technology, integrating advanced systems and new technologies. It will play a crucial role in various Earth observation applications, while also paving the way for future satellite missions.
