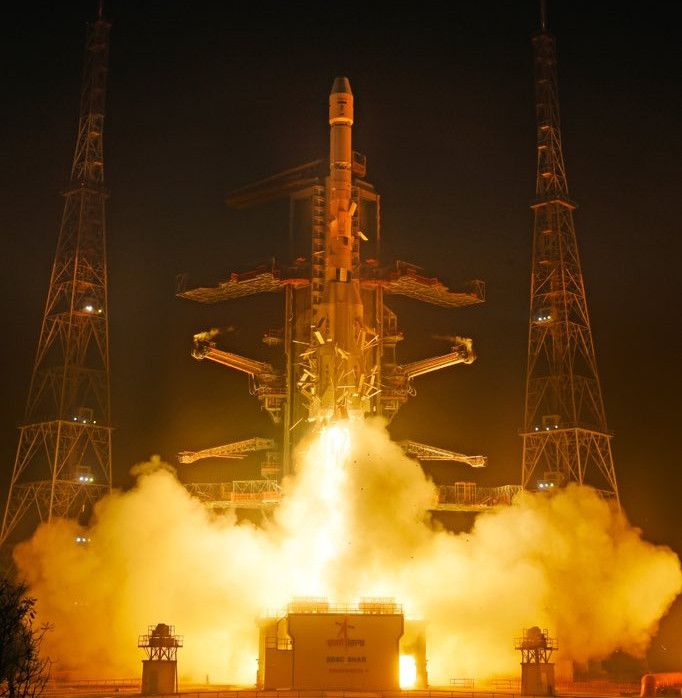

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has achieved another milestone with the successful deployment of the NVS-02 satellite, further strengthening its indigenous navigation system, NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation). This launch marks a significant step in India’s pursuit of technological self-reliance in the realm of space-based navigation.
#100thLaunch:
Congratulations @isro for achieving the landmark milestone of #100thLaunch from #Sriharikota.
It’s a privilege to be associated with the Department of Space at the historic moment of this record feat.
Team #ISRO, you have once again made India proud with… pic.twitter.com/lZp1eV4mmL— Dr Jitendra Singh (@DrJitendraSingh) January 29, 2025
Continuing the Legacy of NVS-01
Following the successful deployment of NVS-01 in 2023, NVS-02 is the second in the series of second-generation navigation satellites designed to enhance the NavIC system.
Both satellites are equipped with advanced navigation payloads operating in L1, L5, and S bands, along with ranging payloads in the C-band. This multi-band approach ensures greater accuracy, reliability, and resilience in positioning and timing services.
A Century of Launches from Sriharikota
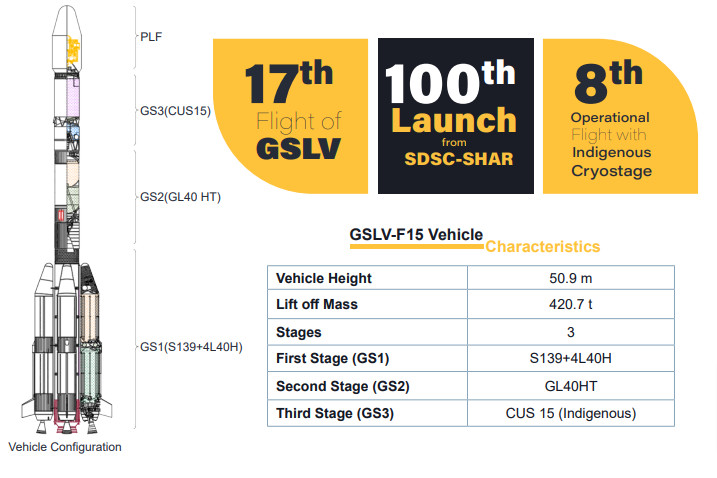
The launch of NVS-02 holds historical significance as it marks the 100th launch from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota. This milestone underscores India’s remarkable progress in space exploration since its first launch, the SLV-3 E1 / Rohini 1A, on August 10th, 1979.
The GSLV, with its indigenous cryogenic stage, has been instrumental in placing heavier payloads into orbit, demonstrating India’s growing prowess in rocket technology.
Enhancing NavIC Capabilities

Positioned at 111.75°E longitude, NVS-02 will replace the IRNSS-1E satellite, ensuring the continuity of NavIC services. With a weight of approximately 2250 kg, it carries a combination of indigenous and procured atomic clocks, crucial for precise timekeeping, which forms the foundation of accurate navigation.
Looking Ahead: The Future of NavIC
ISRO has ambitious plans for the NavIC system, with five second-generation satellites (NVS-01/02/03/04/05) planned to augment the existing constellation.
These satellites will introduce enhanced features and capabilities, ensuring that NavIC continues to provide reliable and precise navigation services to users in India and the surrounding region.
Key Features of NVS-02:
- Advanced Navigation Payloads: Operating in L1, L5, and S bands for enhanced accuracy and reliability.
- Ranging Payload: C-band ranging payload for precise distance measurements.
- Atomic Clocks: A combination of indigenous and procured atomic clocks for accurate timekeeping.
- Orbital Position: Positioned at 111.75°E longitude, replacing IRNSS-1E.
Bus Platform: Configured on a standard 1-2K bus platform with a lift-off mass of 2250 kg and a power handling capability of ~3 kW. - Tri-band Antenna: Employs a tri-band antenna for the navigation payload.
Applications of NavIC:
NavIC offers two types of services: Standard Positioning Service (SPS) and Restricted Service (RS). SPS provides a position accuracy of better than 20 meters and timing accuracy better than 40 nanoseconds over the service area. Key applications include:
Strategic Applications:
- Terrestrial, Aerial, and Maritime Navigation
- Precision Agriculture
- Geodetic Surveying
- Fleet Management
- Location-Based Services in Mobile Devices
- Orbit Determination for Satellites
- Internet-of-Things (IoT) Based Applications
- Emergency Services
- Timing Services
The successful launch of NVS-02 is a testament to ISRO’s dedication and expertise in space technology. It reinforces India’s commitment to developing independent space-based navigation capabilities and providing critical services to various sectors, including transportation, agriculture, disaster management, and defense.
